Home Site Map - Steps - Foundations -
Foundation Concrete Pour - Preparations
![]() All the things that need to be done well ahead of the concrete pour
day.
All the things that need to be done well ahead of the concrete pour
day.
Inspections
Building code requires that the foundation setup be signed off BEFORE any concrete is poured.
Inspection by structural engineer
This is the county licensed structural engineer that did the official structural engineering on the house. He is kept on a retainer to be the official "Engineer Of Record". He does what's called a "special inspection" and writes a one page report that is submitted to the county building department. It just needs to be a signed letter...

Inspection by Building Inspector
This is the county's building inspector. He will have read the inspection report from the Engineer Of Record.

The health department inspector should have already signed off if there is sewer plumbing under the slab.
Do not pour concrete before the inspections have been done!

Checks
Make sure forming is solid
Make sure the forming is good and solid. Wet concrete exerts a considerable force on the forming so it is important to ensure it will not move in any significant way. The main mechanism in my foundation design for resisting the force against the foundation forms is the crushed rock round the outside.
Make sure rebar is securely tied
Wet concrete is heavy and can push rebar out of place if it is not well tied. Make sure the rebar chairs are properly supporting the over-slab rebar and will not move. Make sure the horizontal rebar chairs (that stop the rebar damaging the waterproof membrane at the sides) are positioned properly. Make sure all the vertical bits of rebar that go up into the walls are properly vertical.
Clean up site
Obviously you don't want any trash in the footings or slab area, but it is also good to clean up all round the job site so that nothing gets in the way of the concrete pour.
Get water and detritus out
If it has rained (it will have done) after the waterproof membranes were installed then the footings will have filled up with water as there is no way for it to escape. You will need to use a wet and dry vacuum cleaner and also a submersible pump to get the water out. Also get out any leaves and any other things that may have fallen into the footing trenches.
Ensure good access
Concrete trucks are very large. You need to ensure that there is plenty of room for the concrete mixer to back up to where the building is. A concrete mixer truck is typically 12'6" high. The width of the truck is about 10 feet and the length is 40 feet. They weigh 35 tons, so the roadway needs to be solid so they don't sink in. A pump boom truck needs much more space than a concrete truck. Even a small pump truck needs 20 foot of width to provide for its outrigger feet. The roadway does not need to be much more than say 12 feet wide, but the ground either side must be solid enough to take the outrigger feet. Pump trucks need a huge amount of vertical clearance (say 90 feet), so you need to ensure you can see the sky all the way along your access path and over the site area. There must be no overhead power lines.
Ensure pump truck has level area
The pump truck needs to be level and ideally have its front end slightly lower than its back end/ If necessary dig some holes for where the front wheels will be. Also make sure that there is a stable soil surface where the outriggers will go. If the pump truck operator is a good guy then you might be able to persuade him to bring his truck to site a few days before the pour to get everything figured out.
Ensure concrete truck back end is high enough
The exit point from the concrete truck needs to be at least 18 inches higher than the top of the hopper on the pump truck or else the concrete will not flow down the shoot. In my case I had to implement a ramp using two truck loads of crushed rock (1.25" with fines).
Decide if concrete placer contractor needed
The concrete needs to be pouring all in one day to avoid cold joints. Pouring 19 truck loads of concrete and getting it all flat at the correct slab height in one day needs lots of workers. It needs about 5 or 6 experienced people handling the concrete and another 4 to handle the directing of the concrete trucks and other tasks. If there are more experienced people then the number of hours you need to hire the pump truck will be less. Also, more experienced workers will give a better flatter slab which will mean less shimming when doing the walls and finished floors.
The bottom line is that for a large pour (more than 10 truck loads) it is better to hire-in some experienced concrete workers rather than using friends and family.
Do a search for "Concrete contractors" to find concrete contracting companies in your area. It is worth checking references and online ratings to find a good company. You certainly need to trust them to turn up at the right time.
Things to buy
To some extent this assumes your are doing the concrete placement yourself. A concrete contractor will typically have their own tools.
Concrete vibrator
If you are planning to use concrete a lot then it is worth buying a concrete vibrator as they are expensive to keep hiring. Most concrete vibrators are expensive to buy, but I went with an economically priced one. Details can be found here .
You need to have a concrete vibrator and some kind of backup plan. If you only have one concrete vibrator then you need to think ahead of time what you will do if it breaks. One possibility is to check with a local tool hire place to make sure they have one available if you need to rush down to hire one if your vibrator fails. The best bet is to buy 2 concrete vibrators and that's what I chose to do.
Magnesium Hand Float
These are the hand tool of choice for flattening the top surface of the concrete. Purchasing details are here .
Concrete placer
Concrete placers are used to drag the concrete around to where it is needed.
Long straight 2x4s
These are to use for screeding. Using 2x4s is lighter than using metal bars, but selecting very straight pieces is key. If using a 2x4 longer than about 8 feet then you will probably need a person at each end. Using 8 foot 2x4s is a good choice and can be used by one person.
Wheel barrows
This is if you are using the manual delivery method (which is strongly not advised). Even when using a pump truck it is good to have a couple of wheelbarrows standing by in case you need to go back and fill in some missed spots.
Shovels
Always useful, including directing concrete flow from pump truck tube.
Safety equipment for workers
Need rubber gloves, rubber boots, safety glasses, and hard hats.

Slump test kit
Calculate concrete quantity and implement plan for extra
You need to think in truck loads
Concrete is delivered by the truck load with about 10 cubic yards per truck. The better ready-mix concrete companies will allow you to specify a part truck load for the last truck after you have taken one or more full truck loads.
If your concrete company will not do part loads or if there is too much of a penalty fee for part loads, you may find that you have part of a truck load left over after filling the foundations. If you need to take delivery of the entire truck load, you will need to implement an auxiliary place to put it. Making a concrete patio is one answer. Column pour height can also take up variability.
Calculate the quantity
You need to accurately figure out the volume of concrete needed for the footings and the slab. Split up the foundations into a series of rectangular blocks and add up the amount in each block. You can either do this from drawings or can walk around in the foundations with a tape measure. Note that the dimensions are the inner dimension after all the polystyrene has been installed. For each rectangular block, in feet and decimals of feet, measure the length times the width, then multiply it by the depth. This will give the total cubic feet of concrete required. To convert this number to cubic yards, divide it by 27. The rebar will reduce the amount of concrete slightly but not by much.
Calculation for foundations for small evaluation building
North footing (full length and height): 205 x 28 x 40.5 = 232,470 cu in = 134 cu ft = 4.98 cuyd
South footing (full length and height): 205 x 28 x 40.5 = 232,470 cu in = 134 cu ft = 4.98 cuyd
West footing (reduced length, full height): 83 x 28 x 40.5 = 94,122 cu in = 54.5 cu ft = 2.02 cuyd
East footing (reduced length, full height): 83 x 28 x 40.5 = 94,122 cu in = 54.5 cu ft = 2.02 cuyd
Slab area (not counting footings): 132 x 83 x 9.95 = 101,343 cu in = 59 cu ft = 2.17 cuyd
Total foundation: 16.17 cuyd
Amount left over after 2 trucks (9 cu yards per truck): 1.83 cubic yards
Area of 4" thick concrete patio: 148 sq ft If width is 12 feet, then that's a length of 12 feet.
Calculation for foundations for main house
Backup plan
It's a good idea is to have an alternate concrete project such as a driveway or patio prepared in case a hitch occurs with the pour. You want to ensure the concrete is not wasted.
Forming a concrete patio
For the main house it is useful to have a concrete patio outside the mudroom door.
You should have the patio area formed before the concrete truck arrives. Try to make the design of the patio forming such that you can adjust the area depending on how much concrete is left over.
An acceptable design of concrete patio is 3.5" of crushed rock, then 4" of concrete on top with rebar in it. You can form this using 2x8 lumber (which has a width of 7.5"). At a push for a small patio you can use 2x6s (which are 5.5" wide). Clear the area to get rid of organics and top soil. Stake, and screw the lumber to form the sides. The area formed should constitute your upper estimate of how much concrete will be left over. Ideally implement a movable divider piece of 2x6 within the frame so you can adjust how big an area is filled with concrete.
Use #4 rebar with a 16" pitch in both directions. Support it using about half way up using concrete chairs. Over any disturbed soil, use additional rebar. Make sure any disturbed soil is thoroughly compacted.

Bench furniture
If you just have a small amount of concrete left over then you can also make some concrete benches. The legs of the bench can be done by filling buckets with concrete. The top of the bench can be a piece of 2x12 lumber or you can form a 3.5" thick rectangle to make a bench top or table top.
Make sure concrete trucks can find site

It is also worth doing a map for the last mile that can be given to each driver as someone meets them at the furthest away point. It should indicate where you want them to wait while earlier trucks unload. Also where you want them to go into reverse and where to add the extra plasticizer.
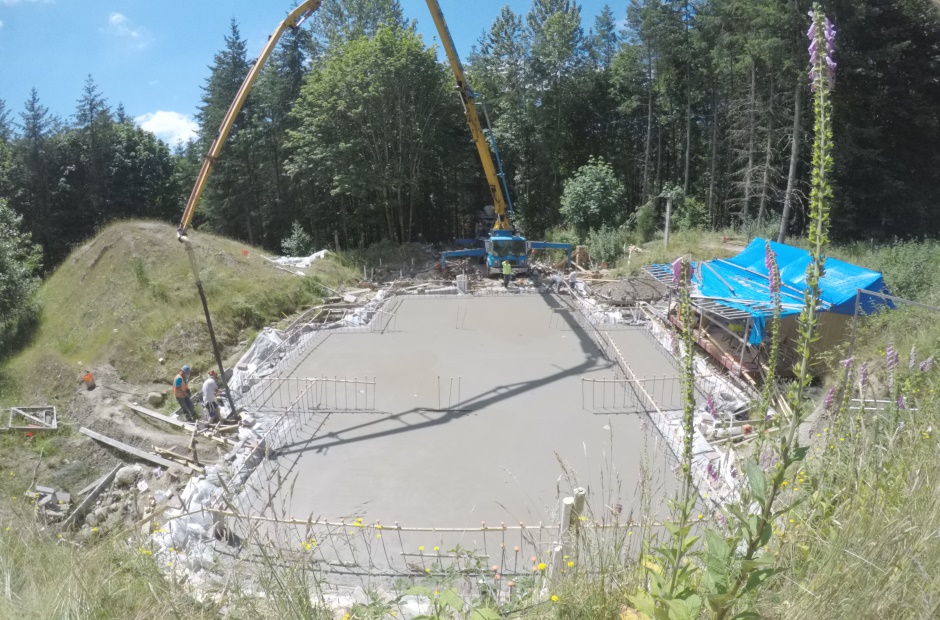
Pour strategy
Start with middle of internal footings so trapped water is forced outwards.
Need to go round footings adding a foot at a time (so that concrete does not separate).
Contractor will do primary vibrating, Family will do extra vibrating.
Family will do directing of trucks to meet Contractor's requirements.
4 columns will be poured with one truck and the shoot a week earlier to check the mix.
Pour easy access deck columns
Pick just the deck columns that can be poured using the simple chute on the back of the concrete mixer truck. Pouring these few columns allows you to check that the concrete that will be delivered to the main house footings is as required.
Do a slump test to allow the concrete deliveries to be compared.
Arrange concrete delivery system (Footings and slab)
You will need a boom pump truck to place the concrete in the foundations. Line pumps are a non-preferred method. Line pumps use pipes and hoses to move the concrete from the truck to the placement location, but require a lot of labor to move the hoses around while in use. A boom truck is like a long arm crane and has a tube all the way up and all the way down to deliver concrete from above just where it's needed. A boom pump costs a little more than a line pump but it's well worth it, particularly as you will save on labor. Pumping concrete for the foundations is easier than with the walls that are higher up, so you can potentially use a line pump for the foundations, but the walls definitely need a boom. Expect to pay about $180 per hour for a boom pump truck.

For the foundations it might theoretically be ok to just back the concrete truck up to near the site and then run a sloping pipe that can be moved around. Note that the feed needs to be moved about rather than just dumping in one place. Dumping in one place causes the mix to separate and be uneven consistency. Concrete trucks have a U shaped chute that comes out at about a 5 or 6 foot height. If you are rigging up your own pipe system, you need some kind of funnel catching arrangement at the start of your pipe arrangement.
Particularly when pouring concrete into ICF blocks, but even when pouring into foundations, it is best to reduce the force with which the concrete exits the hose. It used to be possible to use a reducing device on the end of the pipe but this has now been outlawed for safety reasons by OSHI. Apparently the ungrounded metal ends caused problems. You are still allowed to use a slight reducer just before the flexible pipe end (because it has proper grounding via the metal boom), and this is a good idea. Talk to the pump truck driver to get him to fit this smaller bore pipe. When pumping it is also a good idea to try to kink the end of the pipe yourself to reduce the delivery force.
You will be paying for the boom truck by the hour so coordinating its time on site with the concrete deliveries is critical. You want the first concrete truck scheduled to be 15 minutes later than the boom truck and the next concrete truck 1 hour later. In a 3 hour rental you only actually get about 1hour 45 minutes of pumping because of the 30 minute setup and the 45 minutes of cleanout. That equates to two concrete truck loads (assuming 1 hour between trucks).
Ensure you have all the necessary walkways
In a previous step you will have implemented wooden blocks on the slab area with wooden planks between them. Do a trial walk through of the pour, pretending that you are holding the end of the concrete boom hose and placing the concrete where it is needed. Make sure you have all the necessary walkways to do this. You might also find that a diagonal plank across the center is useful.

Implement a wash-out pond
The pump truck operator will want to have a source of water that they can suck up into the pump to clean it out. They will also want to have a place to dump the washed out concrete. A suitable pond can be implemented by digging a 6'x 6' hole that is about 2 feet deep. Line it with a polyethylene sheet (one continuous waterproof piece). Half fill it with water. You can also use the pond to wash off your concrete tools after the pour.


Arrange for the necessary people
You need plenty of folks to help get the concrete into all the right places and flatten the top surface. It's also worth having at least one person who has taken part in a concrete pour before.
It may be that the company supplying the concrete pumping can provide experienced people (at considerable cost), but typically the pump truck driver will want you to hold and direct the end of the delivery pipe. This is so that there is no liability on the concrete pump operator if anything goes wrong with your job. The pump truck driver will operate the up/down right/left controller for the boom, but they will do so under your direction.
Laser levels
Self leveling lasers are these days the best way of ensuring that you get the concrete top surface level. It is best to get a self leveling laser that shoots out a horizontal line over a wide angle. You can pay a lot for such a laser, but there are also good reasonably priced ones, such as the one that can be found here .
The laser can be positioned in a box that is placed on the slab area. It is designed to keep the beam about 1/8"-1/4" above what will be the surface of the concrete so you can readily see any high spots. The box gets removed after the concrete has set and the hole gets filled in later.

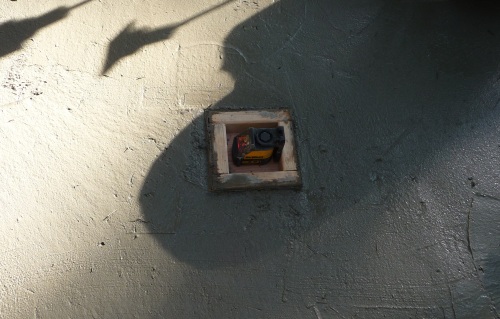
Multiple single point Laser Levels can be used instead if you don't have a self leveling wide beam laser. It's also not a bad idea to use a few low cost fixed lasers as a double check even if you do have a fancy laser. The single point lasers should be placed as needed to shine reference lines across what will be the top of the flat concrete. Given that they are low cost, it is worth checking that they really are shining a totally level beam. Position the beams so that they are about a 1/4 of an inch above where you want the concrete surface.
Check the weather
Having the right weather is important during the concrete pour. The temperature needs to be between 50 degrees F and 90 degrees F (ideally a max temp of 70 degrees F). There must be no rain and no threat of rain. If these weather requirements cannot be guaranteed then you should postpone the concrete delivery.
The higher the temperature, the faster the concrete will set, and very hot conditions will affect the ability of you and your workers to perform.
Order concrete
See the page here that describes the concrete mixture required and other ordering details. Getting the correct concrete mix is important so it is worth studying that page well. It is also vitally important to get the delivery times properly scheduled as you need to have the concrete poured within about 2 hours of it being mixed.










